In recent years, virtual reality (VR) has transcended its origins as a mere gaming technology to become a transformative force across a variety of industries. While gaming remains an important domain, VR has expanded its horizons, providing immersive experiences that redefine how we interact with the world around us. From education to healthcare, architecture to entertainment, VR is revolutionizing many fields and opening up new possibilities for human connection and understanding.
Understanding Virtual Reality:
Before delving deeper into the diverse applications of VR, it is important to understand its fundamentals. Virtual reality creates a simulated environment that immerses users in a synthetic world, typically through the use of specialized hardware such as headsets and motion sensors. By simulating sensory experiences including sight, sound, and even touch, VR transports users into digital realms where they can interact with objects and entities as if they were physically present.
Beyond Entertainment: Diverse Applications Of VR
Education and training:
VR has immense potential to revolutionize education and training by providing immersive learning experiences. Students can explore historical events, dive into complex scientific concepts, or practice real-life skills in simulated environments. For example, medical students can perform virtual surgeries, while pilots can go through flight simulations. VR overcomes physical resource constraints and enhances learning outcomes by promoting engagement and interactivity.

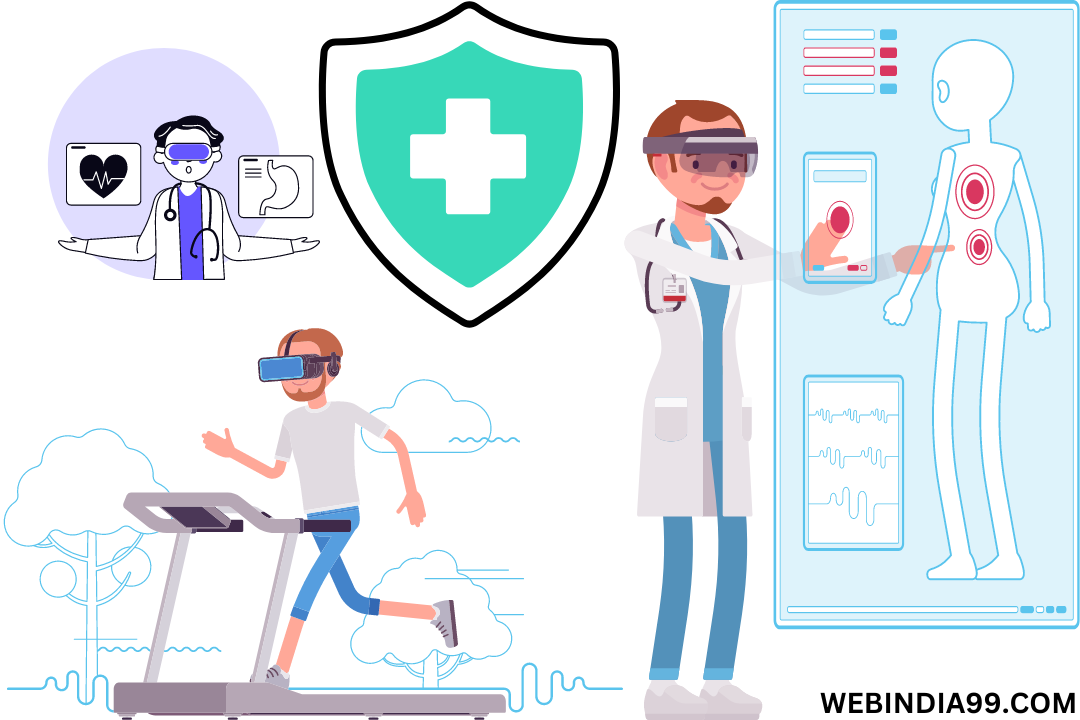
Health care:
In healthcare, VR is demonstrating to be a game-changer. From pain management to therapy, VR applications provide therapeutic experiences that reduce discomfort and enhance patient outcomes. For example, VR exposure therapy is used to treat phobias and PTSD by exposing patients to controlled virtual environments. Additionally, surgeons use VR for preoperative planning and simulation, leading to more accurate procedures and improving patient safety.

Architecture and Design:
VR enables architects and designers to visualize concepts in immersive 3D environments, allowing stakeholders to experience spaces before construction begins. This technology streamlines the design process, facilitates better communication between project teams and enables clients to make informed decisions. By walking through virtual buildings or urban landscapes, stakeholders can assess spatial layouts, lighting conditions, and material choices, resulting in more efficient and aesthetically pleasing designs.

Corporate Training:
VR-based training programs are increasingly being adopted by corporations to increase employee skills and productivity. From customer service scenarios to leadership development simulations, VR enables practical learning experiences that closely resemble real-world situations. By practicing in a virtual environment, employees can hone their skills, make mistakes without real consequences, and gain confidence in challenging situations.

Tourism and Travel:
VR provides immersive previews of destinations, hotels and attractions, revolutionizing the way people plan and experience travel. Through virtual tours and 360-degree videos, travelers can explore destinations remotely, allowing them to make more informed decisions and customize their itineraries. Furthermore, VR experiences can recreate historical sites or natural wonders, providing valuable educational insights and preserving cultural heritage.

Overcoming Challenges and Adapting to Driving:
While the potential of VR is vast, widespread adoption faces a number of challenges, including cost barriers, technical limitations, and concerns about privacy and ethical implications. High-quality VR hardware remains relatively expensive, limiting access to some demographics. Additionally, it is important to ensure seamless integration with existing workflows and infrastructure to maximize the benefits of VR across all industries.
To drive adoption and overcome these challenges, continued innovation is essential. Advances in hardware technology, such as lighter and more affordable headsets, will make VR more accessible to a wider audience. Furthermore, the development of intuitive software solutions and standardized protocols will facilitate interoperability and streamlined implementation across different sectors.

Conclusion: Embracing the VR Revolution:
Virtual reality is no longer limited to the realm of gaming; It has emerged as a powerful tool with far reaching implications for society. By providing immersive experiences beyond physical boundaries, VR is reshaping the way we learn, work, and interact with our environments. From education to healthcare, architecture to corporate


